Direct Current Is Described As
Electrical circuits connect power supplies to loadssuch as resistors, motors, heaters, or lamps. In direct current (dc), the movement of electrical current flows in one constant direction, as opposed to alternating current (ac), in which the current constantly reverses direction.
PPT Lesson 4 Series Circuits and Kirchhoff's Voltage
An example of a device that provides dc current is a battery.
Direct current is described as. There are many different types of batteries used to store electricity and serve as the source of electromotive force. Direct current is described as. The current that flows in a flashlight or another appliance running on batteries is direct current.
Current only flows in one direction. From the graph, we can see that the charged particles in ac tend to start moving from zero. Direct current (dc) power refers to the unidirectional flow of electrons and is the form of power that is most commonly produced by sources such as solar cells and batteries.
Current that flows in both directions is called bidirectional. One advantage of alternating current is that it is relatively cheap to change the voltage of the current. It is used in many household electronics and in all devices that use batteries.
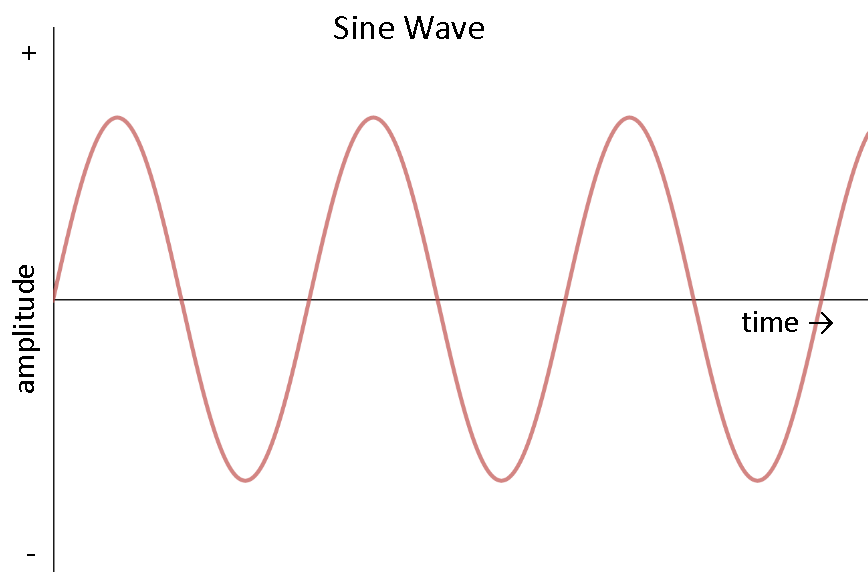
Alternating current is the cyclical flow of electrical current, reversing direction as it flows. It is produced from sources such as batteries, power supplies, solar cells, thermocouples or dynamos. Dc is defined as the unidirectional flow of current;
In alternating current (ac), charges pulse back and forth many times per second as the current moves through the circuit. Direct current is an electric current generated by the charge carriers (electrons) that are flowing in only one direction (backward ← or → forward). Current that flows in only one direction is called unidirectional.
Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through insulators, semiconductors, or vacuum as in electron or ion beams. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. Tesla believed that alternating current (or ac) was the solution to this problem.
Alternating current is described as. Alternating current is described as _____. Alternating current , or ac.
As opposed to alternating current, the direction and amperage of direct currents do not change. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of dc power. Current is described as either direct or alternating, depending on how the charges move through a circuit.
Current that flows in both directions is referred to as _____ current. Direct current (dc) is electrical current which flows consistently in one direction. It is also referred to as _____ current.
Direct current is not easily converted to higher or lower voltages. Direct current means the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is described as.
Current that flows in only one direction is referred to as _____ current. Furthermore, the inevitable loss of energy that occurs when current is carried over long distances is far. Coulomb and electric charge one foundational unit of electrical measurement often taught at the beginning of electronics courses but used infrequently afterward, is the unit of the coulomb , which is a measure of electric charge.
The connection between the supply and the load is made by soldering with wires that are often called leads, or. To simplify things, we will assume that voltage is a constant. The intensity of the current can vary with time, but the general direction of movement stays the same at all times.
The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (ac). In direct current (dc), electric charges always move in the same direction through the circuit. Dc (direct current) is the unidirectional flow or movement of electric charge carriers (which are usually electrons).
By combining electronic controls with Alternating current is produced by rotating magnetic fields like generator s and is the Direct current ultimately supplies power to nearly all electronic devices (even if these devices require a component to convert ac.
In the second volume of this book series, electric circuits are explored where the direction of current switches back and forth: It is the type of current produced by solar panels and get stored in batteries. Direct current is described as.
Voltage and current can vary over time so long as the direction of flow does not change. In a conventional explanation of direct current, direct current can be described as the uninterrupted and constant flow of electricity from a point of negative electromotive force to a point of positive electromotive force. As an adjective, the term dc is used in reference to voltage whose polarity never reverses.
It can also be defined as an electrical current that repeatedly changes or reverses its direction opposite to that of direct current or dc which always flows in a single direction as shown below. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams.
Alternating Current and Direct Current HubPages

Difference Between DCEN Polarity and DCEP Polarity in Arc
PPT Which of the following CANNOT an object's
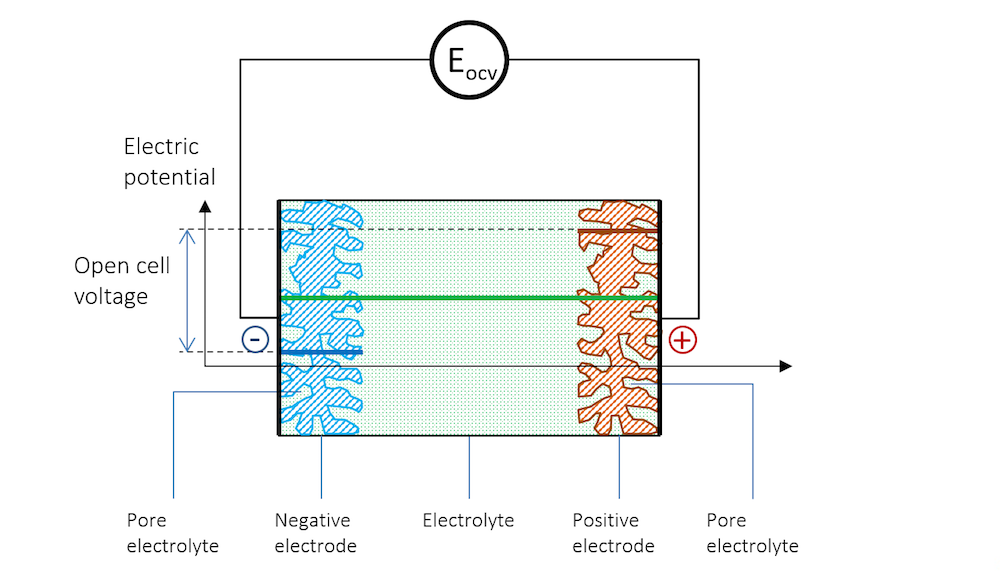
Does the Current Flow Backwards Inside a Battery? COMSOL

Electrolytic Capacitors of 3 Different Kinds News about
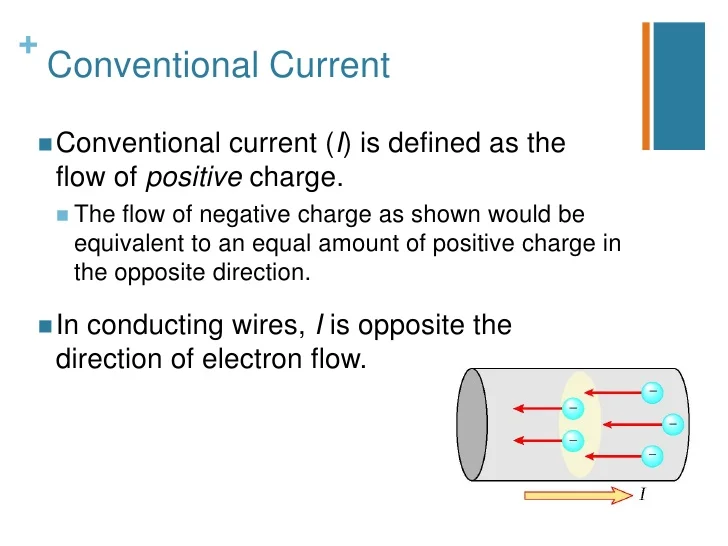
Electrical Energy and Currents
Types Of Alternating and Direct Current Electric Generator
Current flows Electric current

Electricity and Basic Concepts
How does solar power work? Quora

Combining transcranial direct current stimulation and
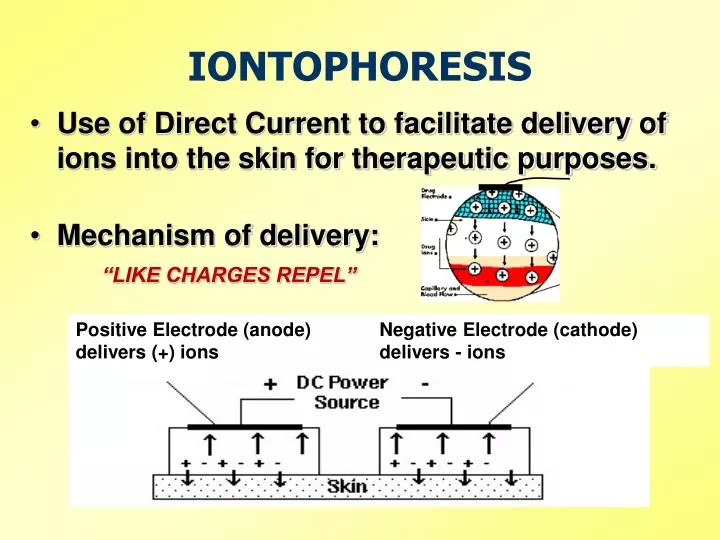
PPT IONTOPHORESIS PowerPoint Presentation ID4526311
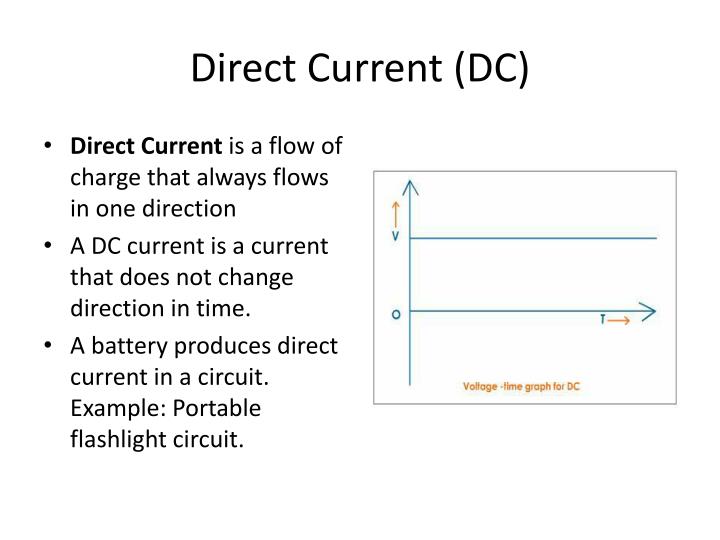
PPT Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC
PPT Principle of Emission Spectroscopy I PowerPoint
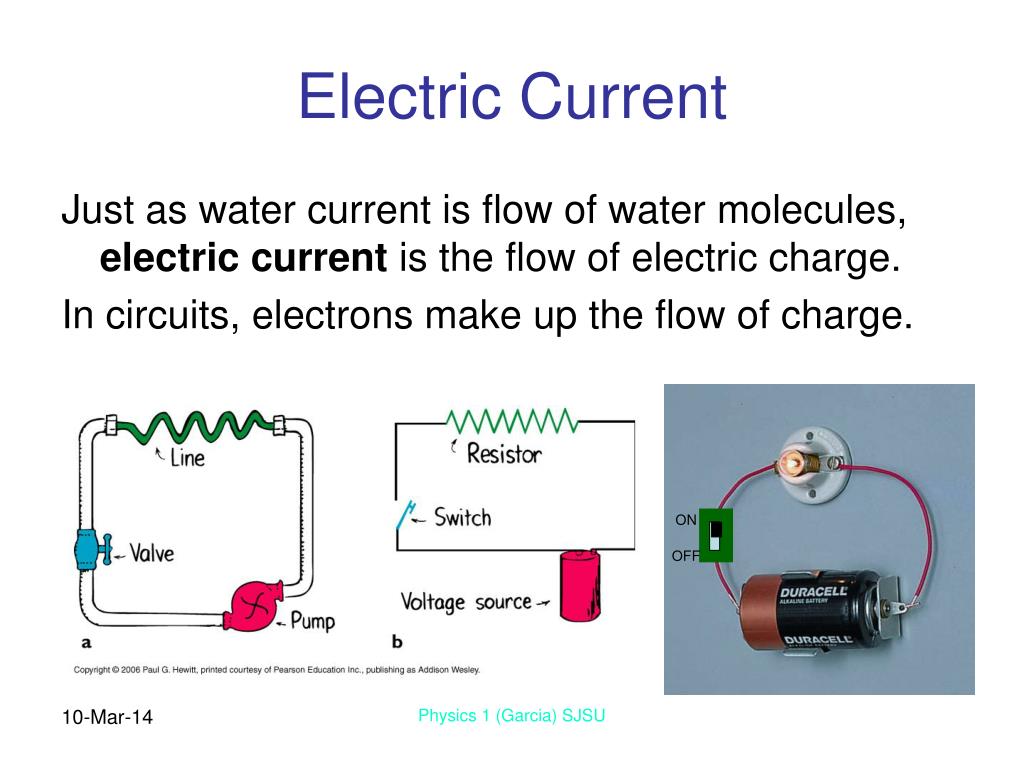
PPT Chapter 23 Electric Current PowerPoint Presentation